- Acetaminophen Is Approved For The Treatment Of Which Conditions
- Acetaminophen Appetite
- Acetaminophen Appendicitis
- Acetaminophen Approved Used
What is this medicine?
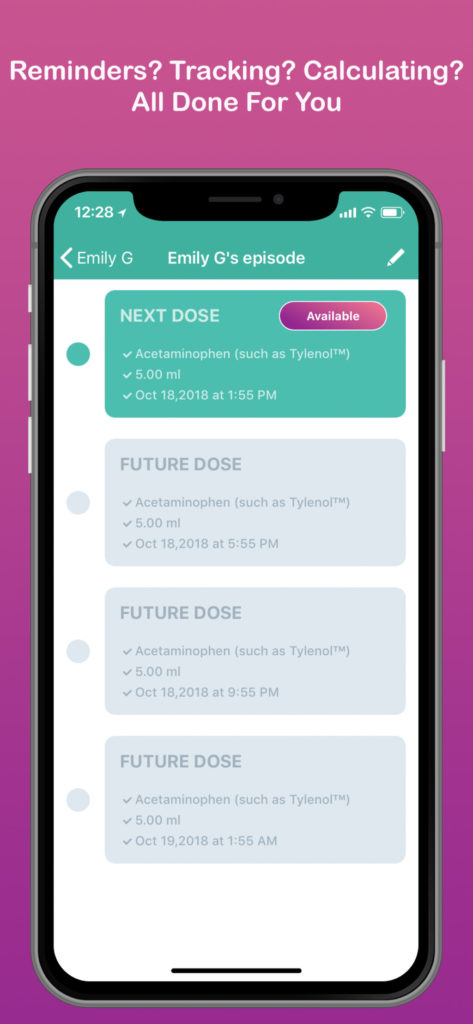
Use our acetaminophen dosage chart to find out how to safely give Infant Tylenol to your feverish or sick baby. APAP is short for N-acetyl-para-aminophenol, better known as acetaminophen or paracetamol. The abbreviation is taken from the initials of the major chemical elements, as shown here in bold: N- a cetyl- p ara- a mino p henol. The substance belongs to a group of pain- and fever-reducing medicines called analgesics.
Taking acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help children with colds and fever feel better. As with all drugs, it is important to give children the correct dose. Acetaminophen is safe when taken as directed. But, taking too much of this medicine can be harmful.
ACETAMINOPHEN; HYDROCODONE (a set a MEE noe fen; hye droe KOE done) is a pain reliever. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain.
How should I use this medicine?
Take this medicine by mouth with a glass of water. Follow the directions on the prescription label. You can take it with or without food. If it upsets your stomach, take it with food. Do not take your medicine more often than directed.
A special MedGuide will be given to you by the pharmacist with each prescription and refill. Be sure to read this information carefully each time.
Talk to your pediatrician regarding the use of this medicine in children. Special care may be needed.
What side effects may I notice from receiving this medicine?
Side effects that you should report to your doctor or health care professional as soon as possible:
allergic reactions like skin rash, itching or hives, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
breathing problems
confusion
redness, blistering, peeling or loosening of the skin, including inside the mouth
signs and symptoms of low blood pressure like dizziness; feeling faint or lightheaded, falls; unusually weak or tired
trouble passing urine or change in the amount of urine
yellowing of the eyes or skin
Side effects that usually do not require medical attention (report to your doctor or health care professional if they continue or are bothersome):
constipation
dry mouth
nausea, vomiting
tiredness
What may interact with this medicine?
This medicine may interact with the following medications:
alcohol
antiviral medicines for HIV or AIDS
atropine
antihistamines for allergy, cough and cold
certain antibiotics like erythromycin, clarithromycin
certain medicines for anxiety or sleep
certain medicines for bladder problems like oxybutynin, tolterodine
certain medicines for depression like amitriptyline, fluoxetine, sertraline
certain medicines for fungal infections like ketoconazole and itraconazole
certain medicines for Parkinson's disease like benztropine, trihexyphenidyl
certain medicines for seizures like carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone
certain medicines for stomach problems like dicyclomine, hyoscyamine
certain medicines for travel sickness like scopolamine
general anesthetics like halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane, propofol
ipratropium
local anesthetics like lidocaine, pramoxine, tetracaine
MAOIs like Carbex, Eldepryl, Marplan, Nardil, and Parnate
medicines that relax muscles for surgery
other medicines with acetaminophen
other narcotic medicines for pain or cough
phenothiazines like chlorpromazine, mesoridazine, prochlorperazine, thioridazine
rifampin
What if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you can. If it is almost time for your next dose, take only that dose. Do not take double or extra doses.
Where should I keep my medicine?
Keep out of the reach of children. This medicine can be abused. Keep your medicine in a safe place to protect it from theft. Do not share this medicine with anyone. Selling or giving away this medicine is dangerous and against the law.
Store at room temperature between 15 and 30 degrees C (59 and 86 degrees F).
This medicine may cause harm and death if it is taken by other adults, children, or pets. Return medicine that has not been used to an official disposal site. Contact the DEA at 1-800-882-9539 or your city/county government to find a site. If you cannot return the medicine, flush it down the toilet. Do not use the medicine after the expiration date.
What should I tell my health care provider before I take this medicine?
They need to know if you have any of these conditions:
brain tumor
Crohn's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or ulcerative colitis
drug abuse or addiction
head injury
heart or circulation problems
if you often drink alcohol
kidney disease or problems going to the bathroom
liver disease
lung disease, asthma, or breathing problems
an unusual or allergic reaction to acetaminophen, hydrocodone, other opioid analgesics, other medicines, foods, dyes, or preservatives
pregnant or trying to get pregnant
breast-feeding
What should I watch for while using this medicine?
Tell your doctor or health care professional if your pain does not go away, if it gets worse, or if you have new or a different type of pain. You may develop tolerance to the medicine. Tolerance means that you will need a higher dose of the medicine for pain relief. Tolerance is normal and is expected if you take the medicine for a long time.
Do not suddenly stop taking your medicine because you may develop a severe reaction. Your body becomes used to the medicine. This does NOT mean you are addicted. Addiction is a behavior related to getting and using a drug for a non-medical reason. If you have pain, you have a medical reason to take pain medicine. Your doctor will tell you how much medicine to take. If your doctor wants you to stop the medicine, the dose will be slowly lowered over time to avoid any side effects.
There are different types of narcotic medicines (opiates). If you take more than one type at the same time or if you are taking another medicine that also causes drowsiness, you may have more side effects. Give your health care provider a list of all medicines you use. Your doctor will tell you how much medicine to take. Do not take more medicine than directed. Call emergency for help if you have problems breathing or unusual sleepiness.
Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen with this medicine. Always read labels carefully. If you have questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Acetaminophen Is Approved For The Treatment Of Which Conditions
If you take too much acetaminophen get medical help right away. Too much acetaminophen can be very dangerous and cause liver damage. Even if you do not have symptoms, it is important to get help right away.
You may get drowsy or dizzy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs mental alertness until you know how this medicine affects you. Do not stand or sit up quickly, especially if you are an older patient. This reduces the risk of dizzy or fainting spells. Alcohol may interfere with the effect of this medicine. Avoid alcoholic drinks.
The medicine will cause constipation. Try to have a bowel movement at least every 2 to 3 days. If you do not have a bowel movement for 3 days, call your doctor or health care professional.
Your mouth may get dry. Chewing sugarless gum or sucking hard candy, and drinking plenty of water may help. Contact your doctor if the problem does not go away or is severe.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Date Last Reviewed: Unavailable
NOTE:This sheet is a summary. It may not cover all possible information. If you have questions about this medicine, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider. Copyright© 2019 Elsevier
Related Conditions
Acetaminophen is a common OTC pain medication used worldwide to relieve mild to moderate pain and reduce fever. Headache, muscle aches, back pain, and menstrual pain are some of the common conditions acetaminophen can be used for using medication management app.
At recommended doses acetaminophen is one of the safest pain medications because unlike other pain relievers, it does not cause stomach or heart problems. For this reason, people who are allergic to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids prefer acetaminophen for pain management.
Acetaminophen is also one of the few pain medications that are safe to use during pregnancy. But, as with all medications using acetaminophen may not be as safe as it seems. It may have some serious risks as well. And according to experts, the risks of using acetaminophen may be far more serious than we realize.
For the most part it could raise the risk of cardiovascular, liver damage, skin allergies, and other conditions.
In this post, we have outlined somecommon risks and benefits of acetaminophen. Read carefully to understand howusing this medication can possibly affect you.
ACETAMINOPHEN BENEFITS
Acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol in many parts of the world, can offer following benefits if taken in safe doses.
Safer Than Other Pain Relievers
Acetaminophen is safer than NSAIDs if taken as per the doctor’s advice. Also, if you don’t have active hepatitis, liver problems, or heavy drinking problems, there is a very slim chance that acetaminophen will harm you.
One of the times acetaminophen can become deadly is when it is combined with another drug because then the user will lose sight of how much of this medication they are taking. As a result they can end up experiencing all the wrong consequences.
Acetaminophen Appetite
Taking too much acetaminophen can result in serious health complications. But again, taking right dose will cause no harm. This is why acetaminophen has become the most widely used analgesic in the world.
On the other hand, NSAIDs come with the risks of developing kidney injury, bleeding, heart problems, and other issues.
Safer Choice for Heart Patients
Taking the right amount of acetaminophen using medication reminder app never has an ill effect on the cardiovascular system. So individuals with the risk of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or those with a history of heart problems can use acetaminophen without worrying about side effects.
On the other hand, prolonged use or higher doses of NSAIDs can increase the risk of blood pressure and heart-related issues. That’s not to say you should not use NSAIDs at all. In fact, they provide a great solution for treating surgery or acute injury pain. NSAID are only dangerous when regularly used for several weeks or months as it can increase the risk of blood pressure and severe cardiovascular issues.
Acetaminophen Is Safe to Use with Aspirin
Aspirin is an NSAID which many people use on a daily basis for heart-related issues. The main job of aspirin is to prevent blood clotting which it does by preventing platelets from sticking together. This, as a result, reduces risk of heart attack and stroke.
Doctors advise against combiningaspirin with non-aspirin NSAIDs because doing so will result in non-aspirinNSAIDs negating the positive effects of aspirin, making your aspirin therapycompletely futile.
Additionally, combining aspirin with non-aspirin NSAIDs for pain management can increase the risks of stomach bleeding, gastritis, kidney injury, and other conditions. So if you are on aspirin and need to manage your pain as well, acetaminophen offers the best solution because it is known to have no negative interactions with aspirin.
ACETAMINOPHEN RISKS
Acetaminophen is generally a safe drug but its improper use can cause several health issues. Therefore, it is important that you use acetaminophen precisely as prescribed by specialists.
The issues caused byacetaminophen include:
Liver Damage
Liver damage is perhaps the mostcommon risk of acetaminophen overdose.
When you take acetaminophen a large part of it is metabolized by the liver and leaves your system through urination. During this process, some of acetaminophen also turns into a toxic metabolite that can harm your liver. Overdosing on acetaminophen can increase the amount of this toxic substance in the liver, which in severe cases, can lead to death.
According to the Food and DrugAdministration (FDA), acetaminophen is one of the leading causes of liverfailure in the U.S. and a large portion of these cases is a result ofaccidental overdoses.
The fact that acetaminophen ispresent in around 600 prescription and non-prescription drugs increases thepossibility of accidental overdose. Particularly for patients taking more thanone acetaminophen-containing drugs at once.
Asthma, Autism, and ADHD in Kids

Though using acetaminophen during pregnancy is considered safe, overdosing on it can be extremely dangerous. Experts say that the use of acetaminophen by expectant mothers can increase the risk of asthma in their children.
However, experts also say this does not warrant changes to current acetaminophen recommendations for expectant mothers, which means that instead of quitting this med, they should consult with their doctors to determine the safe dose they can take using pill tracker app.
Apart from asthma, prenatalexposure to acetaminophen during pregnancy can lead their children to develop autismand attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
So, Is There A Way to Make Acetaminophen Use Less Risky?
In order to reduce acetaminophen’s possible side effects, follow these recommendations:
Acetaminophen Appendicitis
- Use only one acetaminophen-containingproduct at one time
- Take the medication exactlyas prescribed by your doctor
- Keep your daily dose ofacetaminophen below 4,000 milligrams
- Inform your specialist ifyou have liver disease or have experienced liver issues in the past
- Avoid taking acetaminophenif you are a heavy alcohol drinker
- Pregnant women should notuse acetaminophen without doctor’s consultation
Acetaminophen Approved Used
And if you start to notice anyacetaminophen side effects, contact your doctor immediately.